How to Get Started with ESG Reporting
31 July 2024
ESG reporting has evolved from a niche concern to a mainstream requirement.
With increasing regulatory demands and stakeholder expectations, mastering ESG reporting is not just a compliance task; it’s a critical component of sustainable business strategy.
This guide will walk you through the essential steps to initiate ESG reporting in your organization, demystifying the process and providing actionable insights.
What is ESG Reporting?
ESG reporting involves disclosing data related to environmental, social, and governance factors that impact a company’s operations as well as company’s stakeholders including environment.
The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Standard (CSRD) implementation has made ESG reporting mandatory, and the first deadlines are coming soon!
Unlike traditional financial reporting, ESG reporting provides a broader view of a company’s performance, highlighting its commitment to sustainability, ethical practices, and good governance.
Why is ESG Reporting Important?

ESG reporting helps businesses:
- Attract Investors: Many investors now consider ESG factors when making investment decisions.
- Commit to Sustainable Business : Demonstrating a commitment to sustainability can improve brand loyalty and public perception.
- Ensure Compliance: Staying ahead of regulatory requirements helps avoid potential fines and legal issues.
- Drive Performance: Companies with strong ESG performance often exhibit better overall operational efficiency and risk management.
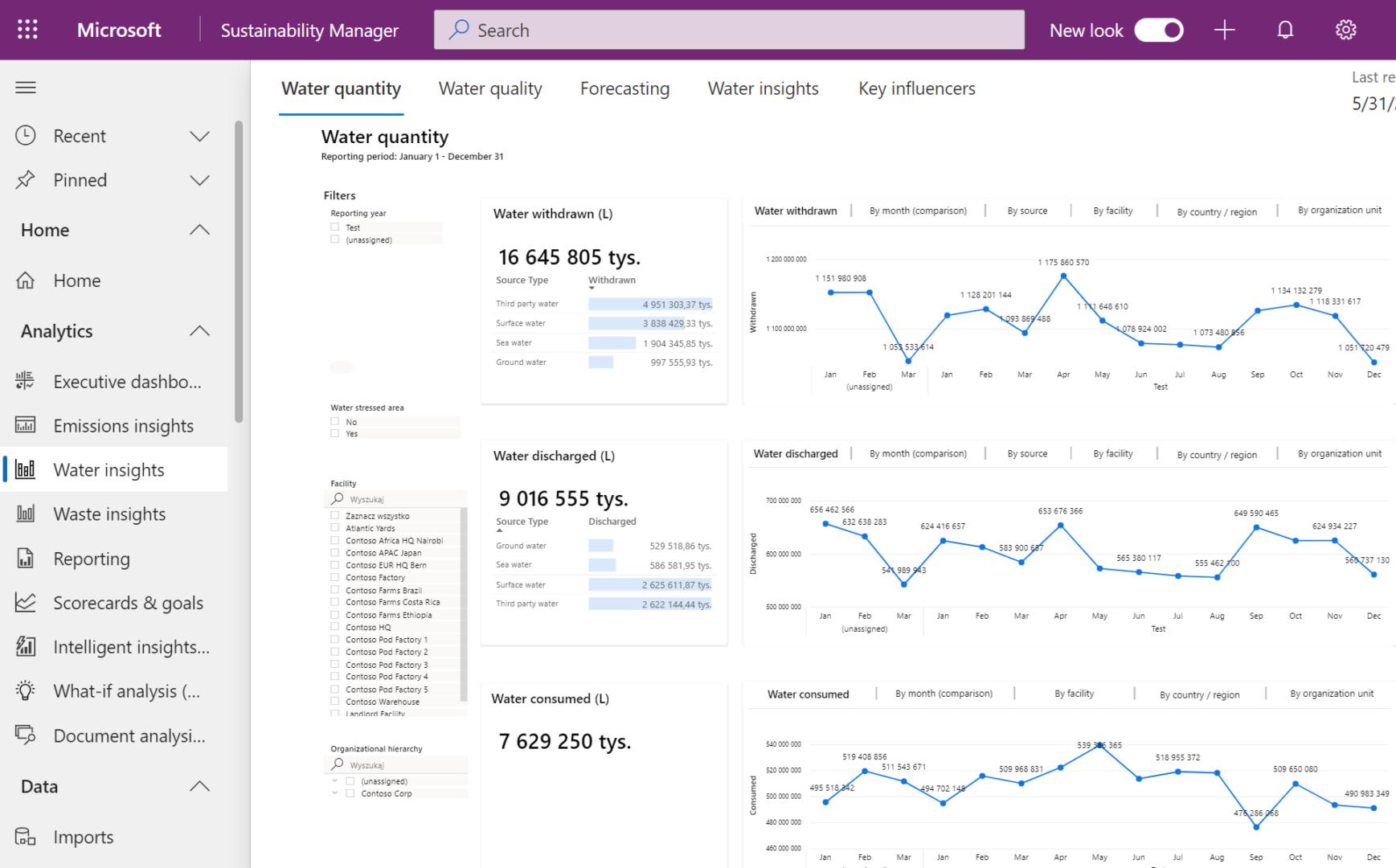
Key Steps to Initiate ESG

1. Understand Regulatory Requirements
As the regulatory requirements in ESG areas continues change, you need to understand the newest requirements applicable for your organization. In EU, following CSRD and conducting reporting according ESRS and EFRAG Implementation Guidelines is a key for success.
2. Assemble a Cross-Functional Team
Form a dedicated ESG reporting team that includes representatives from various departments such as finance, sustainability, legal, and communications. A diverse team ensures that all aspects of ESG are covered and promotes comprehensive data collection and analysis.
3. Engage Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders, both internal and external, in your ESG reporting process. This could include employees, investors, customers, suppliers, and community groups. Engaging stakeholders helps build trust and ensures that your reporting reflects their concerns and expectations.
4. Conduct a Double Materiality Assessment
The double materiality assessment is a critical step in ESG reporting, ensuring that both impact materiality and financial materiality are considered. It comes down to the financial significance for the company and the importance of the company’s impact on the external environment. This involves a systematic process divided into four key phases, as illustrated in Figure 3.
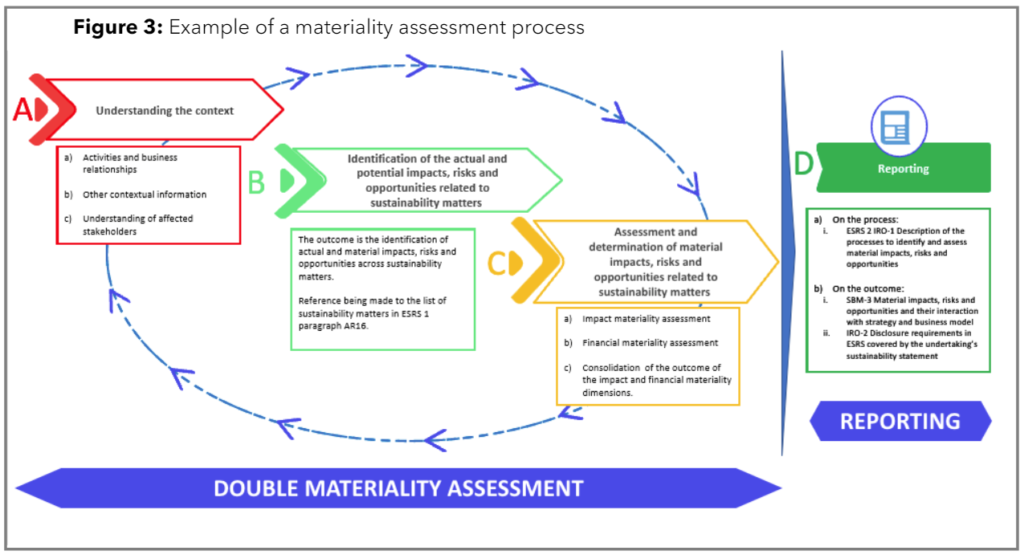
A. Understanding the Context
-
- Activities and Business Relationships: Examine the core activities and business relationships that could impact or be impacted by ESG factors.
- Other Contextual Information: Gather additional relevant information that provides context to the business environment.
- Understanding of Affected Stakeholders: Identify and understand the stakeholders affected by your business operations and their expectations.
B. Identification of Actual and Potential Impacts
-
- Identification of Impacts, Risks, and Opportunities: Determine the actual and potential material impacts, risks, and opportunities related to sustainability matters. This identification process is aligned with ESRS 1 sustainability matters.
C. Assessment and Determination of Material Impacts
-
- Impact Materiality Assessment: Assess the significance of identified impacts from a sustainability perspective.
- Financial Materiality Assessment: Evaluate the financial implications of the identified impacts.
- Consolidation: Combine the results of the impact and financial materiality assessments to gain a comprehensive view of material ESG factors.
D. Reporting
-
- Process Description: Document the process of identifying and assessing material impacts, risks, and opportunities as per ESRS 2 IRO-1.
- Outcome Reporting: Report on the material impacts, risks, and opportunities, their interaction with business strategy, and disclosure requirements as outlined in ESRS.
By following this structured approach, your organization can ensure a thorough evaluation of ESG factors, aligning both financial and sustainability objectives for comprehensive and transparent ESG reporting.
5. Establish a Baseline
Collect historical data to establish a baseline for your ESG performance. This will help you set realistic goals and track progress over time. Make sure to document the sources and methods used to gather this data for transparency.
6. Set SMART Goals and KPIs
Define Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals for your ESG initiatives. Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure progress towards these goals. This will help you stay focused and demonstrate accountability.
7. Develop a Reporting Framework
Create a structured framework for your ESG reporting. Define processes, roles, and responsibilities to ensure consistent and accurate data collection and reporting. Include mechanisms for regular review and updates to keep the framework relevant.
8. Implement Data Collection and Automation
Leverage technology to streamline data collection and management. Use software tools for automated data gathering, analysis, and reporting. This reduces manual errors and ensures timely and accurate reporting.
9. Training & Awareness
Invest in training programs to educate your team about the importance of ESG reporting and how to effectively implement it. Promote awareness across the organization to foster a culture of sustainability and responsibility.
10. Prepare the ESG Report
Compile your data into a comprehensive ESG report. Ensure that the report is clear, transparent, and aligned with the chosen reporting framework. Use visuals like charts and graphs to make the data more accessible and engaging.
11. Internal & External Auditing
Conduct internal audits to verify the accuracy and completeness of your ESG data. Consider engaging third-party auditors for external validation to enhance credibility and trust in your report.
12. Communicate and Disseminate the Report
Share your ESG report with stakeholders through various channels such as your company website, social media, and press releases. Use the report to tell your sustainability story and highlight your commitment to ethical practices.
13. Review and Improve
Regularly review your ESG reporting process and performance. Identify areas for improvement and update your strategies and goals accordingly. Continuous improvement ensures that your ESG efforts remain effective and relevant.
14. Monitor Regulatory Changes
Stay informed about changes in ESG regulations and standards. This will help you adapt your reporting practices to remain compliant and ahead of industry trends.
Over to you
ESG reporting is an ongoing process that requires dedication, transparency, and continuous improvement. By following these steps, your organization can effectively initiate ESG reporting and demonstrate its commitment to sustainability and responsible governance.
Want to take your ESG reporting to the next level? Schedule a demo of our ESG reporting solutions at Elitmind and see how we can support your sustainability goals.
For further insights, check out our articles on ESG Dashboards and ESG Metrics .
This guide has provided a comprehensive roadmap to help you start your ESG reporting journey. If you have any questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team of experts. Together, we can build a more sustainable future.
